Learn everything about Java comments, types of Java comments, Javadoc tool, performance impact of comments and best practices to follow.
Tóm Tắt
1. Why write Java comments?
Java comments, as the name suggests, are notes you write between the programs for various reasons. For example, you may write comments to –
- write information or explanation about the variable, method, class or any statement.
- write text to be available in Java docs.
- hide program code for specific time, etc.
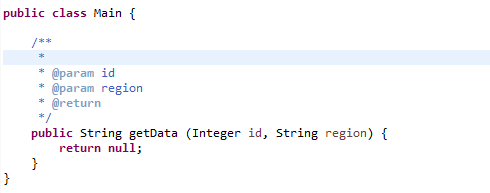
1.1. Java comments example
Given code is an example of Java comments, and how to use them.
/**
* Contains method to greet users by their name and location.
*
* @author Lokesh Gupta
*/
public class Main {
/**
* Launches the application
*
* @param args - Application startup arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
getMessage("Lokesh", "India");
}
/**
* Returns welcome message for a customer by customer name and location
*
* @param name - Name of the visitor
* @param region - Location
* @return - Welcome message
*/
public static String getMessage (String name, String region)
{
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("Hello ");
builder.append(name);
builder.append(", Welcome to ");
builder.append(region);
builder.append(" !!");
return builder.toString();
}
}
2. Types of Java Comments
There are 3 types of comments in Java.
-
Single Line Comment
Use single line comment when comment can be written in a single line only. These comments are written over Java statements to clarify what they are doing.
-
Multi Line Comment
Use multi-line comments when you need to add information in source code which exceeds to more than one line. Multi-line comments are used mostly above code blocks which have complex logic that cannot be written in single line.
-
Documentation Comment
The documentation comments are used when you want to expose information to be picked up by the
javadoctool. This is the information you see in editors (e.g. eclipse) when using autocomplete feature. These comments are pit above classes, interfaces and method definitions.Documentation comment start with
/**and end with*/.You can use javadoc annotations inside these comments e.g.
@paramand@return.Documentation comments are an integral part of programming and should not be skipped.
3. Comment shortcut
In Eclipse IDE, simply typing “/** [Enter]” before a public method or class will automatically generate in all necessary @param, @author and @return attributes.
4. Javadoc Utility
javadoc utility is bundled with JDK distributions. It convert them into standardized, nicely formatted, easy-to-read web pages. It generates API documentation from documentation comments.
4.1. Run javadoc from command prompt
First, make sure javadoc utility is in your PATH. If not then add JDK/bin folder to PATH variable.
$ set PATH=.;C:\BAML\DFCCUI\installs\jdk1.8.0_31\bin
To generate Java docs, execute utility with two arguments. First is location of generated Java docs, and second is Java source files. In our case, I executed this command from location where Main.java is.
$ javadoc -d C:/temp Main.java
It generated these Java docs HTML files.
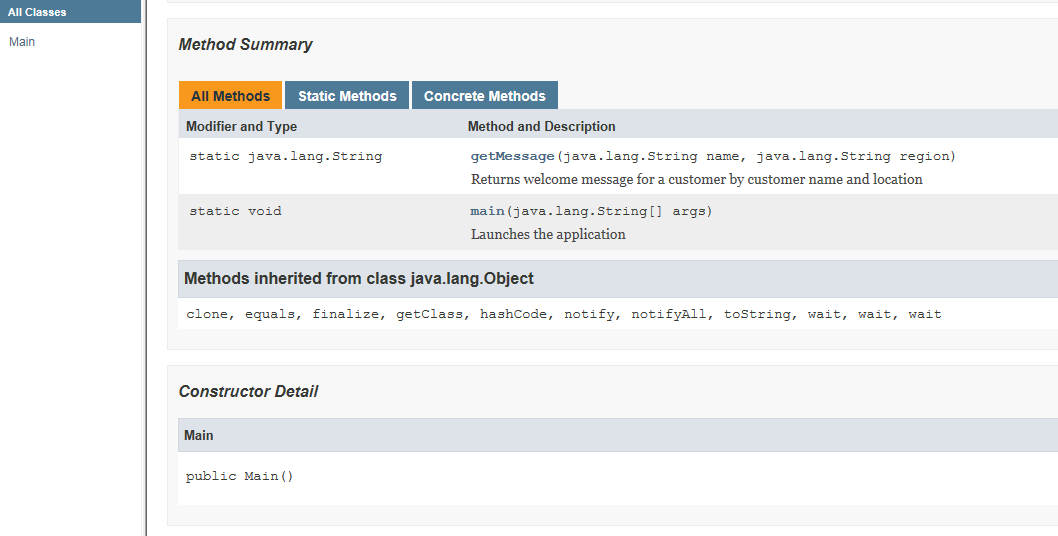
4.2. Run javadoc from Eclipse
You can generate the Java documentation from Eclipse IDE as well. Follow these simple steps-
- In the Package Explorer, right-click the desired project/package.
- Select
Export.../Javadocand clickNext.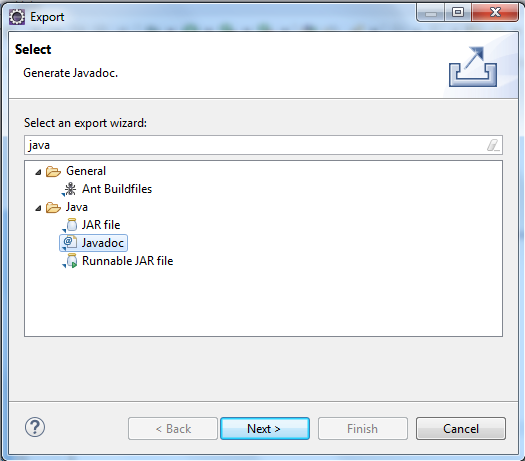
- By default, the entire source code will be selected. Verify and change your selections.
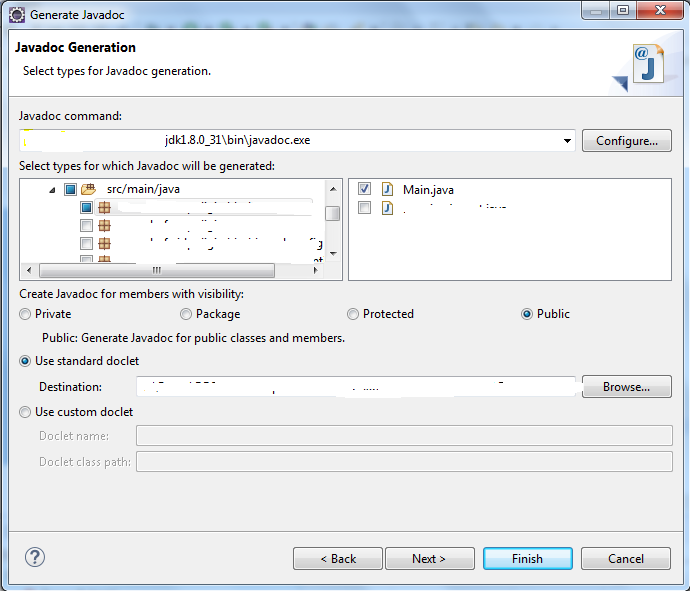
- You may select “
Private” for the visibility level to be generated. This will generate all possible Javadocs, even for private methods. - Select the “
standard doclet” which is the destination folder for your documentation. - Click
Next. - Enter a meaningful
Document titleand clickFinish.
If you follow all above steps correctly, you will have generated Java docs file similar to what we saw in command prompt option.
5. Performance Impact of Java Comments
Implementation comments in Java code are only there for humans to read. The Java comments are statements that are not compiled by the compiler, so they are not included into compiled bytecode (.class file).
And that’s why Java comments have no impact on application performance as well.
6. Java Comments Best Practices
Follow these best practices to have proper comments in your application sourcecode.
- Do not use unnecessary comments in sourcecode. If your code needs more than normal explanation, then possibly re-factor your code.
- Keep comments indentation uniform and match for best readability.
- Comments are for human so use simple language to explain.
- Always add documentation comments in your sourcecode.
Happy Learning !!
Read More-
Oracle recommendations for Javadoc
Javadoc tags reference