
Tóm Tắt
Types of edge devices
One of the most common types of edge devices is an edge router. Usually deployed to connect a campus network to the internet or a WAN, edge routers chiefly function as gateways between networks. A similar type of edge device, known as a routing switch, can also be used for this purpose, although routing switches typically offer less-comprehensive features than full-fledged routers.
Firewalls can also be classified as edge devices, as they sit on the periphery of one network and filter data moving between internal and external networks .This article is part of
What is edge computing? Everything you need to know
Which also includes:
Download1
Download this entire guide for FREE now !In the context of IoT, edge devices encompass a much broader range of device types and functions. Thes e might include sensors, actuators and other endpoints, as well as IoT gateways .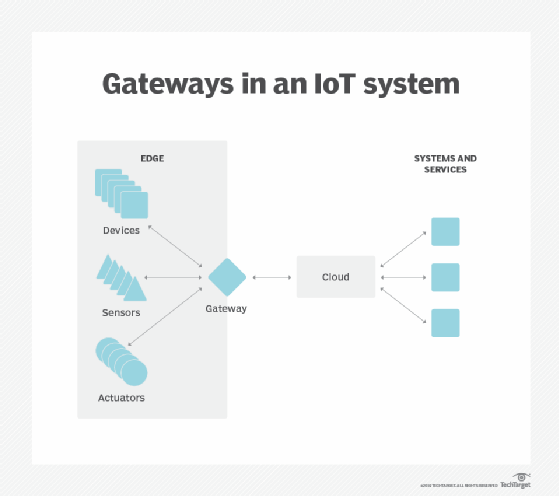 Edge devices encompass a broad range of device types, including sensors, actuators and other endpoints, as well as IoT gateways .Within a local area network ( LAN ), switches in the access layer — that is, those connecting end-user devices to the aggregation layer — are sometimes called edge switches .
Edge devices encompass a broad range of device types, including sensors, actuators and other endpoints, as well as IoT gateways .Within a local area network ( LAN ), switches in the access layer — that is, those connecting end-user devices to the aggregation layer — are sometimes called edge switches .
Edge device use cases
Although the primary function of edge devices is to provide connectivity between disparate networks, the edge has evolved to increasingly support advanced services. These might include the following:
Wireless capabilities. Wireless access points (APs) act as edge devices since they typically provide wireless clients with access to the wired network. Security functions. Edge devices, such as wireless APs or virtual private network (VPN) servers, commonly include integrated security capabilities designed to block a malicious user or device connection. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) services. DHCP is a service that is commonly used in conjunction with edge devices, such as wireless APs and VPNs. When a client connects to such edge devices, the client requires an Internet Protocol (IP) address that is local to the network that it”s accessing. The DHCP server provides the required IP address. In many cases, DHCP services are integrated into edge devices.
Cloud computing and IoT have demonstrated the value for pushing intelligence to the periphery of the network. If an enterprise has thousands of IoT devices, it ” s not efficient for them all to try to communicate with the same resource at once. Edge devices can collect, process and store data in a more distributed fashion and closer to endpoints — hastening response times, reducing latency and conserving network resources .Xem thêm : 1 Gói Xôi Gấc Bao Nhiêu Calo ? Ăn Xôi Gấc Có Béo Không ? Sáng Nào Cũng Ăn Xôi Có Mập Không
How does an edge device work?
As previously mentioned, an edge device is essentially just a bridge between two networks. Thes e can be two on-premises networks, but an edge device can also be used for cloud connectivity. The important thing to keep in mind is that the two networks are otherwise not connected to one another and might have major architectural differences. For example, at one time, it was common for organizations to use Systems Network Architecture ( SNA ) networks for 3270 communications in mainframe environments. As personal computers ( PCs ) and other devices became more prevalent, however, edge devices were used to tie Ethernet networks — or other network types — to existing networks .Regardless of the use case, there are two basic things that an edge device must do. First, the edge device must provide physical connectivity to both networks. The second thing that it must do is allow traffic to traverse the two networks when necessary. Depending on the nature of the edge device, this might mean simply forwarding an IP packet. In the case of architecturally dissimilar networks, however, the edge device might need to perform protocol translation .
Benefits and challenges of edge devices
There are both benefits and challenges associated with the use of edge devices. Some of these include the following :
Expanded access. The primary benefit provided by edge devices is that they enable client devices to access networks and resources that would otherwise be inaccessible. Without a wireless AP — an edge device — for example, wireless clients wouldn”t be able to access resources on the wired network. Device management. One of the primary challenges of operating edge devices is device management. An edge device can enable numerous additional devices to access a network. These devices might not have been registered onto the network, and they could be running operating systems (OSes) that differ from those of devices that have traditionally been used on the network. As such, organizations must consider how best to register and manage these devices. Bottlenecks.An edge device can become a network traffic bottleneck if it fails to provide enough throughput to handle the required network traffic.
Edge device hardware and technology
Initially, an edge device was defined simply as a piece of hardware that enables communications between two networks. Over time, though, edge devices have evolved, with new types of edge devices being introduced. The most notable of these additions is the IoT edge device .
IoT devices are commonly defined as nontraditional, internet-enabled devices that are connected to a network or to the internet. In industrial settings, however, sensors commonly make up the bulk of the IoT devices in use. These might include things such as temperature sensors, moisture sensors or radio-frequency identification (RFID) scanners. Although these types of devices aren”t edge devices, they are commonly connected to an edge gateway. The idea behind this architecture is that, because IoT devices generate data, they must be placed as closely as possible to the systems that use them. Hence, IoT devices commonly send data through a gateway — an edge device — which then passes the data to the computing infrastructure that ultimately stores, analyzes or processes data.
One of the problems that has long plagued IoT devices is that they can generate massive amounts of data. This data must be analyzed if it is to be of use. This can be especially problematic if the data must be uploaded to a cloud service, as doing so incurs direct costs related to the uploading, processing and storage of the data. Depending on the volume of data to be uploaded, the availability of internet bandwidth might also be an issue. Intelligent edge devices, which are sometimes referred to as IoT edge devices, can help with these problems .Xem thêm : Đại Lý Gạo Lứt Huyết Rồng Là Gì ? Giá Trị Dinh Dưỡng Của Gạo Huyết RồngAn intelligent edge device is a sophisticated IoT device that performs some degree of data processing within the device itself. For example, an intelligent industrial sensor might use artificial intelligence ( AI ) to determine whether a part is defective. Other examples of intelligent edge devices include computer vision systems and some speech recognition devices .
Source: https://final-blade.com
Category: Tiền Điện Tử – Tiền Ảo